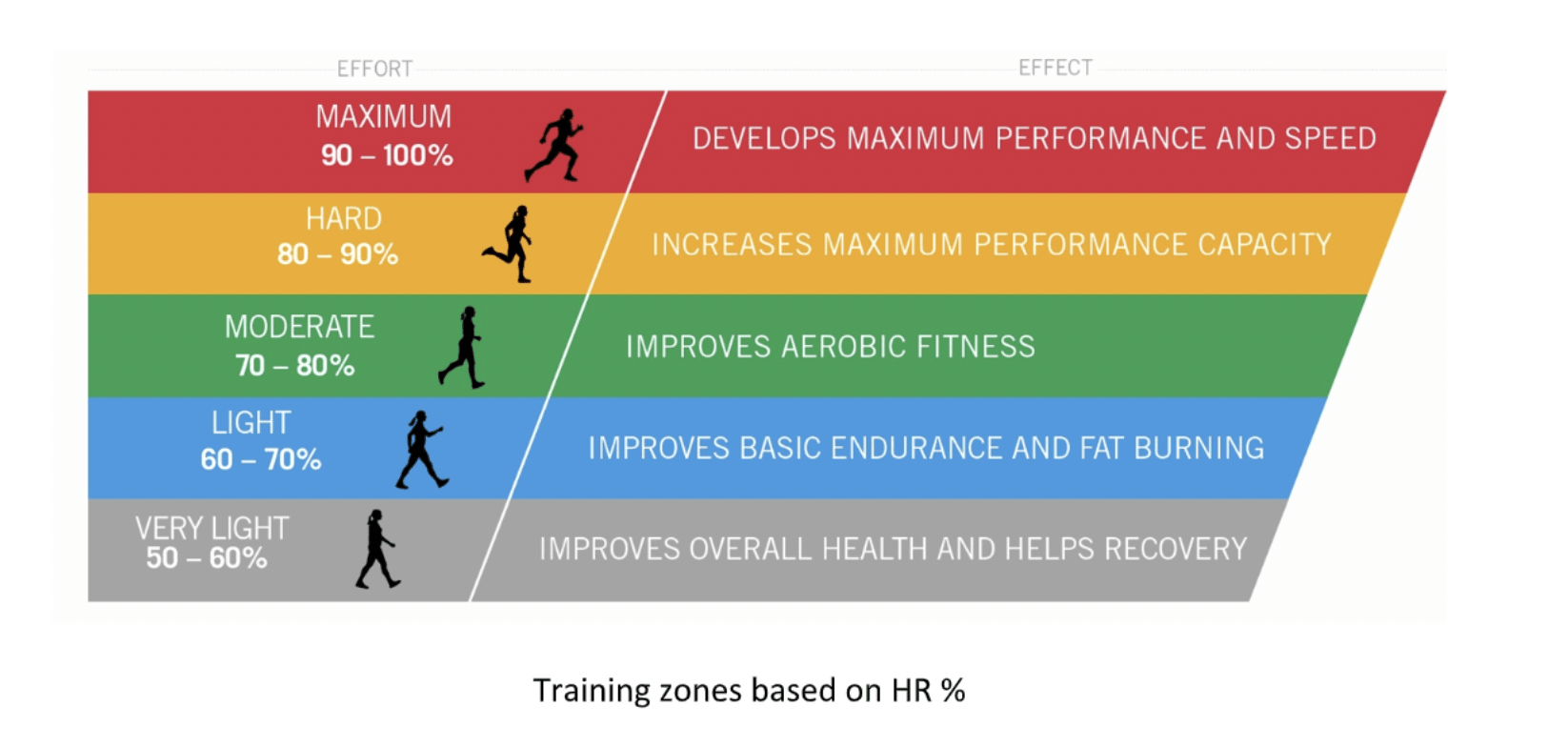
There are five heart rate zones based on the intensity of training with regards to your maximum heart rate. Heart rate zones (HR zones) are a way to monitor how hard you are training. There are different ways to identify your heart rate zones calculation. One simple way is to define them as percentages of your maximum heart rate.
There are five different heart rate zones (1–5) and your training plan should include workouts in all five zones. This HR zones chart shows the level of intensity and percentage of Maximum Heart Rate used in each one.
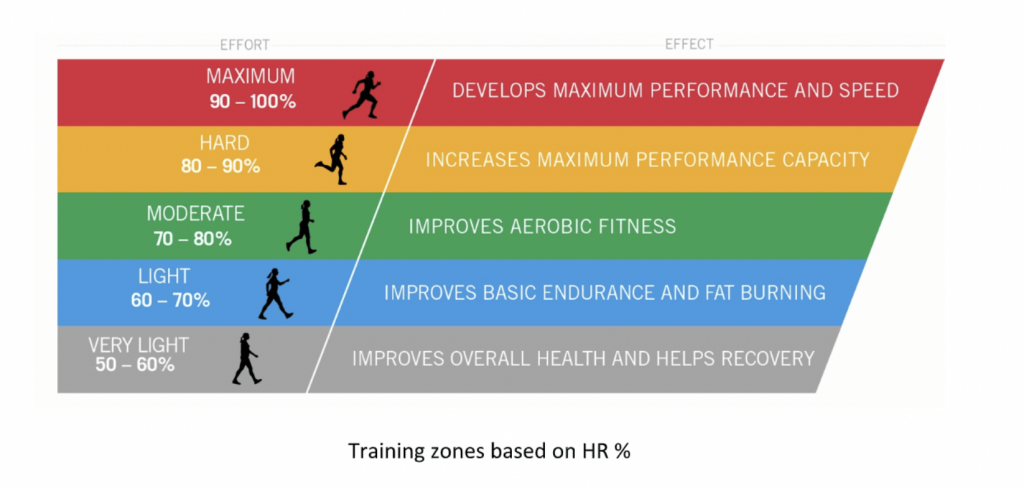
Zone 2 training –
For this blog, we will be focusing on Zone 2 training. “Train slow to run fast” – Zone 2 or low HR training is also one of the best tools to achieve metabolic health and longevity. Exercising in heart rate zone 2 feels light and you should be able to go on for a long time at this intensity. This is the zone that improves your general endurance: your body will get better at oxidizing – burning – fat and your muscular fitness will increase along with your capillary density. Low, zone 2 heart rate cycling, running, rowing, swimming, walking are some of the examples of exercises that one can do within this zone.
Benefits of Zone 2 training –
- Increase in the number of mitochondria
- increase in mitochondrial efficiency
- increase in “metabolic flexibility”
- lower resting heart rate
- a decrease in blood pressure
- lower risk of injury
- improves insulin resistance
- improve your ability to run/cycle longer
- improve your resilience and ability to deal with increasing load.
- Improve your Zone 4,5 function/performance
- improved longevity
When functioning well, our mitochondria uses fat, glucose, and lactate as fuels. In Zone 2, you are using fat oxidation as your primary source of fuel for energy production. In our muscles, we have Type 1 or slow-twitch muscles and Type 2 or fast-twitch muscles. Type 1 fibers have plentiful mitochondria and prefer fat as their source of energy. Type 2 fibers are glycolytic – meaning that they burn glucose. Burning glucose produces lactate. Lactate can be used as fuel if you are well trained. In others, lactate, and an accompanying hydrogen ion build-up. It’s the hydrogen that’s the reason we become exhausted.
In Zone 2 training we want to be firing all our Type 1 fibers and not fire or use our type 2 fibers. We do not want lactate to build up. There is always some glucose being burned… so lactate will rise a bit in zone 2, but it should rise to a point and stay there. This equates to you feeling like you can maintain your efforts for a long time. Once you recruit your Type 2 muscle fibers, you will start to fatigue. The rate at which you fatigue is variable. That rate will depend on how well trained you are, and how well your mitochondria clear the lactate.
To maintain aerobic fitness and endurance, zone 2 training can be beneficial for all age groups. Our PTs at all locations can help all individuals regardless of their health conditions to design a training program for maintenance and overall fitness. Ask your PT about zone 2 training at your next appointment!